Emotive Journeys
AI-Powered experience that connects therapeutic arts with emotional expression
Team Jenn Choi, Latisha Sanders
Team contributions
- Jenn: UI/UX Design, Prototyping, Frontend Development, Emotion-driven Interaction Design, System Architecture
- Latisha: Research, Creative Arts Therapy, UI/UX Design and Project Management.
Link to Pre-Activity Prototype: https://oculus-outer-07751739.figma.site/
Link to Prototype: https://grain-luxury-01901327.figma.site
Pre-Activity Prototype Design Process: From the image to design, I developed a personalized emotional color palette by first guiding users to select an emoji that best represents their current mood, followed by choosing colors from the color wheel that reflect those feelings. These inputs are then mapped onto a 2D emotional model, allowing the system to interpret emotional tone through color psychology. Based on this combined emoji-and-color analysis, the prototype generates a customized palette that visually captures the user’s emotional state and supports deeper self-awareness through intentional color selection.
Experience Steps
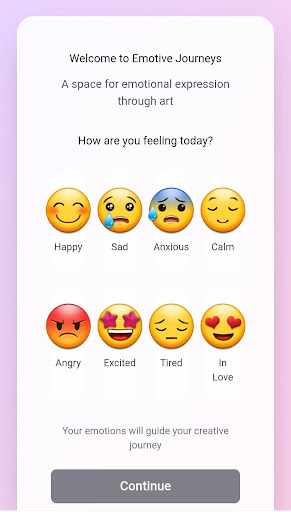
1. Emoji Emotional Tracker:
On the Welcome/Onboarding screen, the user will be be asked “ How are you feeling today?” to help them recognize how they are feeling. This will also help to provide a visual representation of their current emotional state and enhance active engagement with the activities.
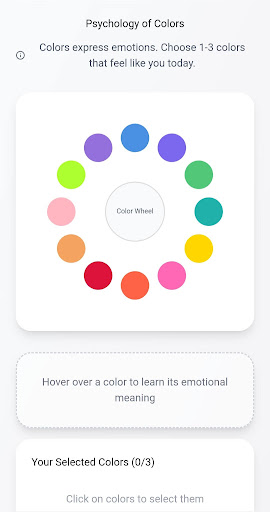
2. Color Wheel/ Psychology of Colors- Color based activity with emotional association:
Colors are associated with different emotions and is a form of non- verbal communication. Emotions and the relationship between colors will be represented in a visual tool called a color wheel. Users will be asked to choose emotions that best describe their current feelings, so that they can connect their feelings with their current emotional state. This will be done to encourage them to connect their feelings to specific situations, thoughts and triggers and allow them to reflect and focus on what matters most during the drawing session rather then trivial thoughts or memories. They will use the colors that they chose during the drawing session with the AI chat companion. This will allow for intentional and impactful art in order to enhance emotional expression and evoke feelings in their art. The AI chat companion will also provide an description on the meaning of the colors they selected and ask the user questions (ex. Why did you choose this color?) about the colors they selected. This will be done to help cultivate an opportunity to exchange open dialogue and create a safe space for emotional tracking and journaling as part of the therapeutic process.
3. Emotional Visualization
The system maps the selected color and emotion into a 2D emotion model (Pleasure–Arousal grid or color emotion wheel). → A brief visual feedback (“You’re in the calm zone today “) reinforces reflection.
4. Personalized Palette Generation
Based on the user’s emotional state, the system generates a custom palette and transitions to the sketchbook interface. → “Start your sketch with today’s color mood” appears with a smooth fade-in animation.
5. Guided Expression (AI Chat Companion)
Once inside the sketchbook, the AI companion (e.g., Luma) starts a brief empathetic dialogue: “I sense you’re feeling calm today. Would you like to create something peaceful or expressive?” → The chat dynamically adapts tone and suggestions (scene ideas, brush types, or color blending) based on the user’s earlier emotional data.
6. Creative Flow & Reflection Loop As the user draws, the AI companion provides gentle emotional prompts or reflections—e.g., “This blue gradient feels very serene. Would you like to add a touch of warmth to balance it?” → These prompts encourage mindful observation and emotional awareness throughout the sketching process.
Project Scope
Target Learning Audience: Young adults who are struggling with mental health issues, and a secondary target audience for individuals who are particularly interested in therapeutic arts
Identified Learning Need For our project, we would like our target audience to be young adults who are struggling with emotional mental health issues. Mental health awareness is a pivotal issue among young adults. The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) statistics shows that young adults (age 18–25) have the highest rates of mental illness. We would like to address these issues through the lens of art inquiry and creative arts therapy. We will create an interactive virtual art experience, which will include an in-person component that can be implemented by a young adult icon to create engagement and enhance reliability or a tour guide. We hope this app will support young adults by equipping them with therapeutic skills on how to navigate their emotional issues through creativity and art (visual art, poems, music, and digital takeaways).
Rationale for AI Assistance • Recommendation of content tailored to user emotions via sentiment analysis algorithms (e.g., comforting poetry, color-based art suggestions, music generation) • Detection of negative emotional patterns and guidance on emotion regulation techniques to facilitate creative shifts • Establishment of a human-AI collaborative socio-emotional learning environment to enhance interaction between users and offline components (guides or leaders) AI can provide enhanced digital support, such as offering positive content for users. This will allow AI to create algorithms to identify and analyze emotional cues from user input. AI can guide users through therapeutic techniques that help manage and reduce negative emotions and thought patterns by applying creative art outlets. We also want to implement a social-emotional element within our app that will work as a human-AI collaborative learning experience. This will allow the user to interact with the in-person component to enhance engagement and socio-emotional awareness and development.
References: • Shojaei F, Shojaei F, Osorio Torres J, Shih PC. Insights From Art Therapists on Using AI-Generated Art in Art Therapy: Mixed Methods Study. JMIR Form Res. 2024 Dec 4;8:e63038. • Li, X., Kim, J., & Patel, S. (2024). Exploring the Use of ChatGPT as an AI-Based Emotional Support Agent for Mental Health Assistance. Computers in Human Behavior, 158, 108–122. • National Institute of Mental Health. (2024). [Mental Illness]. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health [Internet]. Retrieved October 6, 2025, from [https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/mental-illness]
Needfinding
Learner Needs
- There is a need to detect negative emotional patterns to address and help identify recurring negative thoughts and behaviors.
- There is a need to enhance interaction between users and digital support content and identify which digital support elements should be implemented to address this need. This will help to create progress tracking and personalized activities for a more personalized and effective experience.
- There is a need to implement a social emotional element to work as a social emotional element that will provide an impactful human AI collaborative experience for users. Implementing a social element through dialogue and social interactions promotes collaborative learning because this allows users to have the opportunity to use communication as an expression of their independent thoughts. The collaboration creates connections and a flow for users to engage with digital content and acquire meaning making.
- There is a need to build trust and emotional continuity between users and AI systems to sustain long-term engagement and authentic emotional expression. Immediate empathy is beneficial, but users also require consistent tone, memory of prior interactions, and emotional reliability to feel safe sharing their thoughts over time.
Literature Review
- Insights From Art Therapists on Using AI-Generated Art in Art Therapy (Shih et al., 2024)
Art therapists affiliated with the American Art Therapy Association participated in this study evaluating how AI can be integrated as a digital tool in therapy. They developed a prototype using cards with emotion-based keywords (emotions, feelings, relation, companion, environment, visual) and AI-generated images via ChatGPT and Adobe Express. Participants found that this tool helped them visualize and express emotions, improving confidence and creative expression throughout their emotional journey. Similar to this study, our project uses AI as a tool for emotional regulation, helping users feel secure as they process feelings and express themselves creatively.
- Exploring the Use of ChatGPT as an AI-Based Emotional Support Agent for Mental Health Assistance (Li et al., 2024)
This study explores ChatGPT’s role as an emotional support tool, identifying both its potential and limitations. Researchers found that ChatGPT’s empathetic language and immediate feedback enhanced users’ ability to articulate emotions and reflect on their thoughts. However, the study also noted the lack of emotional persistence and relational trust. These insights inform our project’s design: building a system that remembers emotional context, responds consistently with empathy, and promotes emotional continuity.
Pain Points Identified:
- Lack of emotional continuity — short-term empathy but no long-term memory of emotional context.
- Limited trust-building — users hesitate to open up repeatedly without relational consistency.
- Surface-level understanding — AI struggles with complex emotional nuances.
Relevance to Our Project:
I think this literature directly supports our project’s focus on AI-assisted emotional expression and poetic creation. It shows how ChatGPT helps users verbalize and externalize emotions, aligning with our goal of transforming emotional states into poetic language. It also points out that AI lacks emotional persistence and relational depth, reinforcing our design direction to build a system that remembers emotional context and responds with consistent empathy. Overall, I think this research provides a solid foundation for positioning AI not just as a tool, but as an emotional collaborator that co-creates meaning with users through dialogue, reflection, and shared creativity.
Link for Design Feature Map:
Ethics Chart
| Ethical Principle | Key Questions | How are you considering this ethical principle in your work? | |———-|:————-:|——:| | Privacy | If the users talk about their private stories with AI, how can we analyze their feelings without keeping the data and learning it? | If the users talk about their private stories with AI, how can we analyze their feelings without keeping the data and learning it? | | Responsibility | If a negative outcome results from using this tool, who is responsible? | The user will be responsible for negative outcomes. However, these outcomes will be evaluated to determine what caused the negative outcome and modified on an as needed basis.| | Beneficence | What benefits might result from using this tool?|The intent for this tool is that users will be able to monitor their emotions and identify triggers that are causing them to have negative feelings.|
Early Prototypes
Initial prototyping focused on establishing core functionality:
Phase 1: Individual Feature Design Individual features were designed separately and tested for usability before integration. Each component (drawing tools, emotion detection, chat interface) was developed in isolation to ensure robust functionality.
Phase 2: Layout Composition Features were composed together on a single screen to establish overall layout structure and user flow. This revealed the need for clear visual hierarchy between expression (drawing) and reflection (AI feedback) stages.
Phase 3: Basic Functionality Early versions focused solely on drawing capabilities without emotion analysis, serving as a baseline for user interaction patterns.
Design Process
Initial Layout Design & High-Fidelity Prototyping After establishing the feature set, I created a high-fidelity prototype in Figma. The design was iteratively refined using Figma’s AI prompting feature for rapid iteration. Elements that proved difficult to modify through prompts were designed separately in Figma and manually positioned, allowing for precise control over complex interface components.
API Integration OpenAI’s API was connected to enable functional chat interaction. Initial testing confirmed successful basic conversation functionality, establishing the foundation for more sophisticated contextual awareness development.
UI Enhancement & Interaction Design To improve user interaction and create a more immersive experience, I implemented several visual enhancements:
• Dynamic speech bubble colors that respond to emotional context, providing subtle visual feedback • Gradient backgrounds in the chat interface to create atmosphere and emotional resonance • Intuitive visual cues that guide users naturally through the emotional exploration process
These refinements aimed to make the experience more immersive and intuitive for users engaging with their emotions, reducing cognitive load and supporting natural interaction flow.
Emotion Meter Logic Development (~25% of Development Time) This phase proved to be the most technically challenging aspect of the project.
Initial Challenge: The AI struggled to interpret user drawings accurately, often producing inconsistent emotion readings. Early testing revealed the system was not reliably distinguishing between different emotional expressions.
Key Insight: Through extensive prompting experimentation, I discovered that the AI primarily recognized colors first, leading to similar emotion classifications regardless of form or composition. This meant the system was over-relying on color analysis—for example, interpreting any drawing with predominantly blue tones as “calm” regardless of whether the forms were chaotic or composed.
Solution: I rebalanced the analysis algorithm by:
- Reducing color analysis weight in the overall emotion calculation
- Increasing form analysis importance
- Adding multiple visual cue detection including: • Facial expressions (when present) • Line thickness and stroke intensity • Drawing speed (inferred from stroke patterns) • Screen coverage ratio (fullness vs. emptiness) • Composition balance and use of negative space
This multi-factor approach significantly improved accuracy and consistency in emotion detection, creating more meaningful and personalized feedback.
AI Conversation Refinement The final major technical refinement addressed the AI’s contextual understanding during conversations.
Challenge: The AI initially lacked sufficient contextual awareness during user conversations, leading to disconnected or less relevant responses. It would sometimes respond generically without acknowledging the specific emotional nuances the user had expressed through their drawing.
Iterative Improvement: Through continuous prompt engineering, we refined: • What the AI should read and prioritize from user inputs (emphasizing emotional content and drawing patterns) • The appropriate tone and nuance for responses (supportive, non-judgmental, inquiry-based) • Contextual awareness across conversation threads (maintaining memory of previous exchanges and drawing sessions)
This iterative prompting process improved the AI’s ability to provide contextually appropriate and emotionally supportive responses that felt genuinely attuned to the user’s state.
4. PROTOTYPE
Final Prototype Description
The completed Emotive Journeys prototype guides users from visual expression to emotional reflection through an integrated, AI-powered experience.
User Journey
Initial Emotion Identification (Pre-screen) Users begin with a brief emotion-identification step that establishes baseline emotional awareness and primes them for deeper exploration.
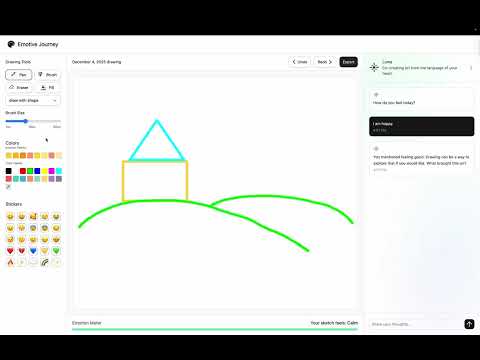
Drawing Canvas - Visual Expression The core interaction centers on the drawing canvas, where users freely express their current emotional state through visual creation.
Features:
- Multiple brush types supporting varied expression styles (line, spray, texture)
- Full color palette with adjustable saturation and hue
- Stroke weight and opacity controls for nuanced expression
- Responsive touch/mouse interaction for natural drawing feel
- Real-time visual feedback with no lag or performance issues
The interface is designed to encourage low-pressure, intuitive creation without technical barriers or artistic skill requirements.
Emotion Meter - Real-Time Analysis As users draw, the emotion meter continuously analyzes their work based on:
- Color Analysis: Temperature (warm/cool), saturation (vibrant/muted), and contrast
- Form Analysis: Stroke patterns, line quality, shape recognition
- Composition: Spatial distribution, balance, use of negative space
- Dynamic Cues: Drawing speed (inferred from stroke density), pressure simulation through line thickness
The system categorizes emotional states into high-level affective groups:
- Calmness (cool colors, balanced composition, gentle strokes)
- Tension (sharp lines, high contrast, compressed space)
- Overwhelm (high coverage, chaotic patterns, intense saturation)
- Focus (concentrated elements, deliberate strokes, clear structure)
What Works: The balanced multi-factor algorithm provides consistent, meaningful emotional readings that users report align with their subjective experience. The real-time updating creates a feedback loop that helps users see how their creative choices reflect emotional states.
AI Conversation - Reflective Dialogue Based on the drawing analysis, the AI generates contextually appropriate conversation that supports reflection.
AI Feedback Includes:
- Highlighting emotional cues identified in the artwork (“I notice the concentrated use of warm colors in the center”)
- Suggesting alternative interpretations (“This could represent both energy and urgency”)
- Providing gentle prompts for self-reflection (“What does the empty space on the left represent for you?”)
- Recognizing patterns across sessions (when applicable)
What Works: The AI successfully maintains conversational context, responds with appropriate emotional tone, and frames feedback as suggestions rather than diagnoses. Users report feeling heard and guided rather than judged or analyzed.
Immersive Visual Design Throughout the experience, dynamic UI elements enhance immersion:
- Speech bubble colors shift subtly based on conversation emotional content
- Background gradients respond to overall emotional tone
- Smooth transitions guide users from expression to reflection stages
- Clear visual hierarchy prevents confusion about interface state
What Works: The cohesive visual language creates an atmosphere conducive to emotional exploration. Users report the experience feels “contained” and “safe,” supporting vulnerable self-expression.
Technical Implementation
- Frontend: Figma for design, with AI-assisted iteration for rapid prototyping
- Backend: OpenAI API for conversational AI and emotion analysis
- Drawing Engine: HTML5 Canvas with custom brush rendering
- Emotion Detection: Custom algorithm balancing color psychology, form analysis, and compositional principles
- Data Flow: User drawing → Visual analysis → Emotion categorization → AI prompt generation → Conversational response
Features That Work Successfully
✓ Drawing canvas provides responsive, intuitive creative expression ✓ Multi-factor emotion meter delivers consistent, meaningful analysis ✓ AI conversation maintains context and provides non-prescriptive feedback ✓ Visual design creates immersive, emotionally supportive atmosphere ✓ User flow naturally progresses from expression to reflection ✓ System performs reliably without technical errors or lag
Known Limitations
• Emotion meter logic could be more transparent to users • Post-drawing summary screen would enhance closure • Mobile/tablet pressure sensitivity not yet implemented • Session history and pattern tracking across multiple uses not yet developed